Sensors and biosensors have revolutionized clinical engineering and hospital management by providing accurate detection and monitoring of biological and environmental parameters. In this article, we will explore the technological advancements of these devices and their impact on healthcare.
Índice del Articulo
What are sensors and biosensors?
Sensores:
Sensors are devices designed to detect and measure changes in their physical environment and convert this information into electrical or digital signals. In the context of clinical engineering, sensors can be used to measure various biological, physical, or chemical variables that are relevant to health monitoring and medical diagnosis.
In clinical engineering, sensors are critical for data acquisition that is used in medical devices and patient monitoring systems. They can measure variables such as body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, glucose level, among others. These devices convert physical signals into interpretable data, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately track a patient’s condition.
Biosensors:
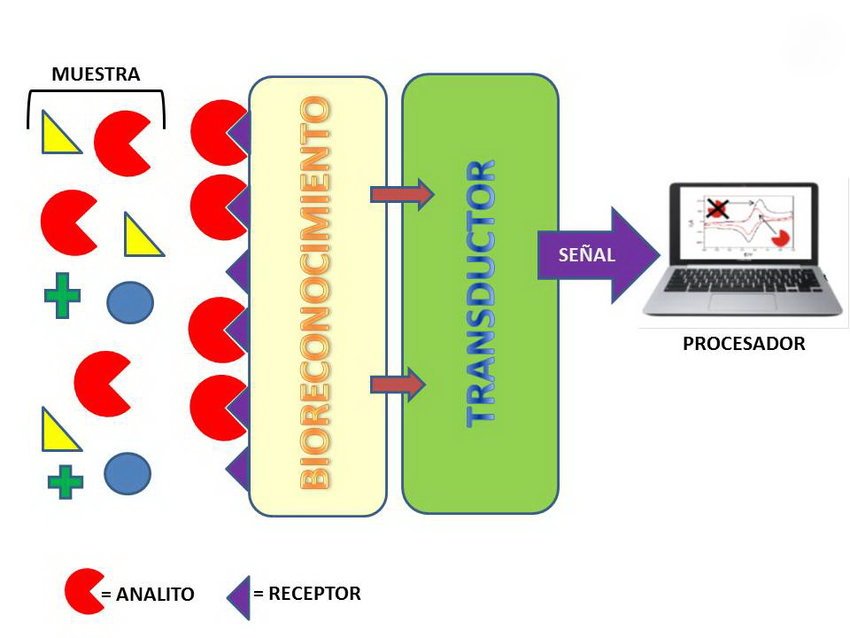
Biosensors are analytical devices that combine a biological component with a transducer to detect and convert a specific biological response into a quantifiable signal. In the clinical setting, biosensors often use enzymes, antibodies, or other biological molecules to recognize and measure biomarkers relevant to disease diagnosis or monitoring.
Biosensors are valuable tools in medical applications due to their ability to provide highly specific and sensitive measurements. For example, a biosensor could be employed to detect the presence of certain molecules in a blood sample, facilitating early diagnosis of disease. These devices play a crucial role in personalized medicine and chronic disease management by enabling more accurate and continuous monitoring of key biological indicators.

What are the applications in clinical engineering of Sensors and Biosensors:
Applications of sensors and biosensors in clinical engineering are diverse and cover a wide spectrum of medical areas. Here are some key applications:
Sensors in Clinical Engineering:
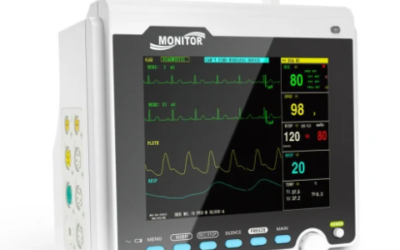
- Vital Signs Monitoring: Sensors embedded in medical devices to measure and monitor vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, body temperature, and blood pressure.
- Glucose Monitoring: Sensors used in glucose meters for continuous monitoring of glucose levels in patients with diabetes, allowing for more precise control and adjustments in treatment.
- Respiratory Monitoring: Sensors in devices that record respiratory rate and oxygen saturation, which is crucial in monitoring patients with respiratory problems.
- Medical Imaging Sensors: Sensors used in medical imaging equipment, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans, to capture detailed images of the inside of the body for diagnostic purposes.
- Position and Motion Sensors: Sensors used in surgical navigation technologies to track the position and movement of surgical instruments during complex procedures.
Biosensors in Clinical Engineering:
- Infectious Disease Diagnosis: Biosensors that detect the presence of specific biomarkers of infectious diseases, facilitating rapid and accurate diagnoses.
- Continuous Monitoring of Biological Markers: Implantable or portable biosensors that allow continuous monitoring of biological markers, such as troponin for monitoring cardiac events.
- Cancer Detection: Biosensors that identify specific cancer markers in biological samples, contributing to early detection and treatment monitoring.
- Drug Control: Biosensors used to monitor the concentration of drugs in real time in the body, ensuring therapeutic levels and avoiding toxicity.
- Biosensors for Coagulation Monitoring: Biosensors that measure blood coagulation activity, being crucial in the management of anticoagulants and patients with coagulation disorders.
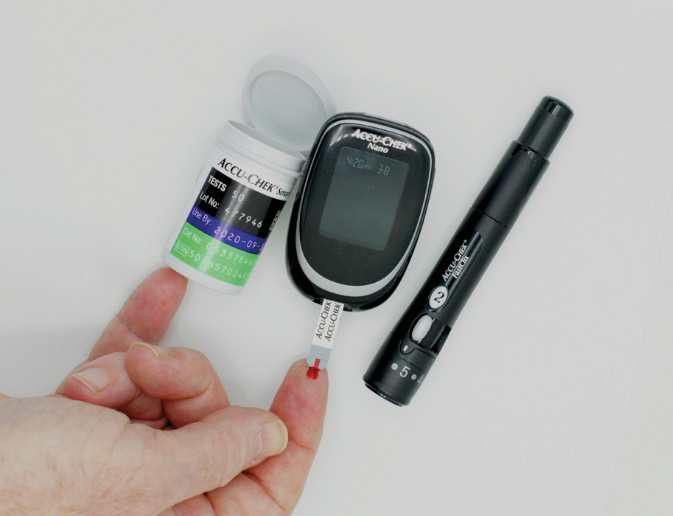
What are the advantages of using sensors and biosensors in hospital management:
The use of sensors and biosensors in hospital engineering offers several advantages that contribute significantly to the efficiency, accuracy and quality of healthcare. Here are some of the key advantages:
Advantage of sensors in Hospital Engineering:
- Continuous Monitoring: Provides continuous monitoring of vital signs and other clinical variables, allowing early detection of changes in the patient’s condition.
- Process Automation: Facilitates the automation of hospital processes, such as medication administration, temperature control, and medical equipment management, improving efficiency and reducing human errors.
- Resource Optimization: Enables more efficient management of hospital resources by providing real-time data on bed occupancy, equipment availability, and facility utilization.
- Improved Patient Safety: Contributes to patient safety by alerting on critical conditions and providing accurate data that helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Facilitates more advanced diagnostics through high-quality medical images and accurate measurements of clinical parameters, which is essential for the treatment and monitoring of diseases.
Advantage of biosensors in Hospital Engineering:
- Rapid Disease Detection: Enables rapid and specific detection of diseases by identifying biomarkers, which is crucial for early initiation of treatment.
- Personalized Medicine: Facilitates personalized medicine by providing detailed information on patient response to specific treatments, allowing for precise adjustments in therapy.
- Reduced Response Times: Contributes to reduced response times in critical situations by providing real-time measurements of key biological parameters.
- Continuous Monitoring of Key Markers: Enables continuous monitoring of relevant biological markers, such as glucose, lactate or troponin, which is essential for patients with chronic or critical illnesses.
- Reduced Invasiveness in Diagnostic Tests: Many biosensors allow for less invasive diagnostic tests compared to traditional methods, improving patient comfort and reducing the risk of infections.

Technological advances in sensors and biosensors:
Technological advances in sensors and biosensors have been significant in recent decades, driven by innovation in science and technology. Some of the most notable advances include:
Technological advances in sensors in hospital engineering:
- Wireless Sensors and IoT: Integration of wireless sensors into Internet of Things (IoT) systems, allowing remote patient monitoring and instant data transmission to healthcare professionals.
- Wearable Sensors: Development of sensors integrated into wearable devices, such as smart watches and bracelets, that constantly monitor physiological data and allow continuous health monitoring.
- Nanosensors: Advances in the miniaturization of sensors at the nanometer scale, allowing applications in personalized medicine and early detection of diseases at the molecular level.
- Advanced Imaging Sensors: Improvement in the resolution and precision of sensors used in medical imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, allowing more detailed diagnoses.
- Environmental Sensors in Hospital Environments: Implementation of environmental sensors to monitor air quality, temperature and other factors in hospital environments, contributing to infection prevention and patient well-being.
Technological advances in Biosensors in Hospital Engineering:
- Implantable Biosensors: Development of implantable biosensors that can constantly monitor biomarker levels in the body, providing real-time information and facilitating personalized treatments.
- Paper Biosensors and Portable Devices: Creation of inexpensive and easy-to-use paper biosensors and portable devices for rapid disease detection and continuous monitoring of biological parameters.
- Flexible and Biocompatible Biosensors: Design of flexible and biocompatible biosensors that can be integrated with biological tissues, allowing applications in regenerative medicine and long-term health monitoring.
- Multi-Marker Biosensors: Development of biosensors capable of detecting multiple biomarkers simultaneously, improving diagnostic accuracy and monitoring of complex diseases.
- Nanotechnology in Biosensors: Integration of nanotechnology in biosensors to improve the sensitivity and specificity of detection, allowing earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Frequently asked questions about Sensors and Biosensors:
What is a sensor in the context of clinical engineering?
A sensor in clinical engineering is a device that detects and measures physical, chemical or biological parameters in the medical environment to monitor the health status of patients or the operation of medical equipment.
What is the difference between a sensor and a biosensor?
A sensor measures physical or chemical parameters, while a biosensor uses biological components to detect specific substances, such as enzymes or antibodies, offering greater specificity for clinical applications.
What are the most common sensors in medical devices?
Temperature, pressure, oxygen, glucose and electrocardiogram sensors are common in medical devices to monitor vital signs and conditions of patients.
How are clinical sensors calibrated?
Calibration is performed by comparing sensor readings to known values. In clinical settings, this is done regularly using calibration standards and adjusting the sensor as needed.
What is the importance of accuracy in medical sensors?
Accuracy is critical to ensure that readings are reliable and accurate, which is essential for making informed medical decisions.
How does external interference affect biosensors?
External interference can affect the selectivity and sensitivity of biosensors. The use of selective coatings and advanced technologies helps to minimize this problem.
What challenges do biosensors face in continuous monitoring?
Long-term stability, rapid response and biocompatibility are key challenges. Research is focused on addressing these aspects to improve the effectiveness of biosensors.
How is the safety of implantable sensors ensured?
Implantable sensors must meet strict safety standards. The use of biocompatible materials, extensive testing, and the implementation of low-power technologies are common practices.
What recent advances have been made in the miniaturization of medical sensors?
Advances include smaller, low-power sensors and wireless devices, facilitating integration into wearable devices and enabling more continuous and comfortable monitoring.
How do sensors contribute to telemedicine and remote healthcare?
Sensors enable real-time data collection, facilitating remote monitoring of patients. This is essential for telemedicine and remote healthcare, improving access to healthcare.
Conclusion on Sensors and Biosensors:
Sensors and biosensors represent a key technology in clinical engineering and hospital management. Their ability to measure and monitor biological and environmental parameters accurately and in real-time has improved healthcare, allowing for early detection of disease and more effective intervention. As technological advancements continue, these devices are expected to play an even more crucial role in improving healthcare and hospital management.
Recommendation:
To deepen your knowledge of clinical engineering, I suggest you continue reading the next article that addresses: What is the Department of Clinical Engineering?




0 Comments