The Clinical Engineering Department is essential in the management and maintenance of medical technology in hospitals. In this article, we will explore its importance, functions, and benefits in delivering quality healthcare services.
Índice del Articulo
Medical Technology Management in Clinical Engineering:
Medical technology management in Clinical Engineering is a specialized field that deals with the planning, implementation, maintenance, and continuous improvement of medical equipment and systems in healthcare settings. Some key aspects of medical technology management are described here:
Technology Inventory and Assessment:
- Conduct a complete inventory of all medical equipment.
- Assess obsolescence and condition of existing equipment.
- Establish priorities for upgrading or replacing technologies.
Acquisition and Evaluation of New Technologies:
- Collaborate with healthcare professionals to identify technology needs.
- Evaluate new technologies prior to acquisition, considering aspects such as interoperability and regulatory compliance.
Strategic Planning:
- Develop short- and long-term strategic plans for medical technology management.
- Integrate technology into the institution’s overall healthcare strategy.
Technology Implementation and Integration:
- Coordinate the installation and commissioning of new medical equipment.
- Ensure effective integration of technology with other systems and workflows.
Preventive and Corrective Maintenance:
- Establish preventive maintenance programs to ensure optimal equipment performance.
- Manage corrective maintenance interventions efficiently.
Regulatory and Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure that all equipment complies with relevant rules and regulations.
- Coordinate inspections and audits to maintain compliance.
Data Management and Security:
- Implement security measures to protect the integrity and confidentiality of medical data.
- Manage system interoperability to facilitate data exchange between teams.
Performance Evaluation:
- Establish metrics to evaluate the performance of medical equipment.
- Use data to make informed decisions about upgrades, replacements, or changes in medical technology management.
Life Cycle Management:
- Plan the useful life of medical equipment and technologies.
- Develop strategies for the timely replacement or upgrade of obsolete equipment.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration:
- Collaborate closely with health professionals, biomedical engineers, administrators and others to ensure comprehensive management aligned with institutional objectives.
Medical technology management in Clinical Engineering is essential to ensure the availability, efficiency and security of the technology used in the delivery of healthcare services. A systematic and proactive approach to this management contributes to the continuous improvement of patient care and operational effectiveness in hospital and healthcare environments.
Maintenance and calibration in Clinical Engineering:
Maintenance and calibration in clinical engineering are crucial aspects to ensure the safe and accurate operation of medical equipment used in healthcare environments. Key concepts related to maintenance and calibration are described here:
Preventive Maintenance:
Preventive maintenance is defined as a set of planned activities performed on a regular basis with the goal of preventing failures, ensuring reliability, and prolonging the life of medical equipment. These practices include inspections, cleaning, lubrication, adjustments, and replacement of parts according to a predefined schedule.
Corrective Maintenance:
Corrective maintenance refers to interventions carried out to correct faults or defects identified during the normal use of equipment. This type of maintenance involves diagnosing problems, repairing components and restoring the equipment to its normal operating state.
Inventory and Spare Parts Management:
Inventory and spare parts management involves maintaining an up-to-date inventory of spare parts and components. Associated practices include efficient spare parts management to reduce downtime and ensure the availability of critical components.
Asset Management:
Asset management in the medical field involves the comprehensive administration of equipment, considering aspects such as its useful life, total cost of ownership, and decision-making on renewal or replacement. Associated practices include strategic planning based on the asset life cycle and the specific needs of the institution.
Calibration:
Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of a measuring instrument against a reference standard. Practices associated with calibration include parameter adjustment, verification of readings, and recording of results obtained during the process.
Regular Calibration:
Regular calibration refers to a planned and systematic program to calibrate medical equipment at regular intervals. Practices associated with this process include compliance with calibration protocols defined by both the equipment manufacturer and applicable regulations.
Calibration Certification:
Calibration certification is formal documentation that ensures that equipment has been calibrated and meets established accuracy standards. Practices associated with calibration certification include issuing detailed certificates that provide information about the calibration procedure, the results obtained, and the date the process was carried out.
Traceability and Standards:
Traceability and standards in calibration refer to ensuring that the standards used are linked to recognized national or international standards. Associated practices include the use of calibration instruments and procedures that comply with established regulations and standards.
Measuring Equipment Management:
Measuring equipment management involves effective management to ensure the timely calibration and maintenance of such equipment. Associated practices include recording calibration histories, managing certificates, and scheduling calibration intervals.
The effective combination of maintenance and calibration ensures that medical equipment operates reliably, providing accurate measurements and precise clinical results. Implementing systematic and documented practices in these two aspects is critical to meeting regulatory standards, maintaining patient safety, and optimizing operational efficiency in healthcare settings.
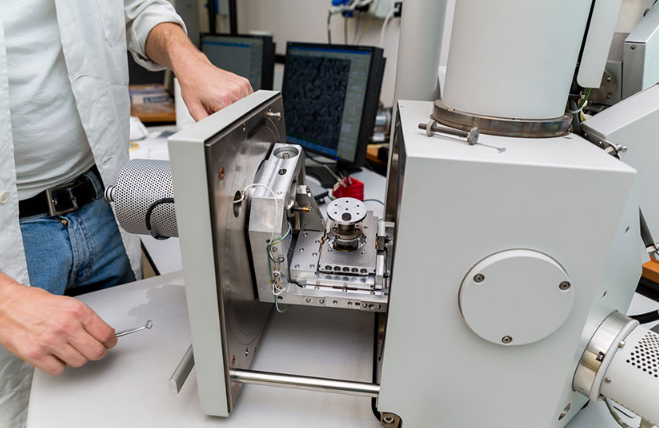

Technical support and training in Clinical Engineering:
Technical support and training are essential elements in the field of Clinical Engineering to ensure the effective operation of medical equipment and the continuous development of staff. Key aspects related to technical support and training in Clinical Engineering are detailed below:
Remote and On-Site Support:
Remote support involves providing remote technical support to resolve issues and perform diagnostics. In contrast, on-site support involves coordinating technical visits when it is necessary to address issues that cannot be resolved remotely.
Incident Management:
Incident management involves systematic logging and documentation of issues. In addition, a tracking system is established to ensure effective and timely resolution of documented incidents.
Updates and Patches:
Update and patch management involves providing software and firmware updates to improve equipment performance and security. In addition, proactive deployment of security patches and bug fixes is carried out.
Coordination with Manufacturers:
Coordination with manufacturers involves maintaining effective communication with them to obtain technical assistance and updates. In addition, participation in technical support programs offered by manufacturers is highlighted as a key practice.
Staff Training:
Staff training includes providing initial training to users and technicians on the proper use and maintenance of medical equipment. The importance of offering ongoing training programs to keep staff up to date on the latest technologies and best practices is also highlighted.
Technical Skills Development:
Technical skills development involves the implementation of specific programs for biomedical engineers and clinical engineering staff, with the aim of improving their technical skills. In addition, the importance of facilitating opportunities to obtain relevant certifications in the field is highlighted.
Simulations and Practical Training:
The use of simulations and practical training involves using simulated scenarios to train staff in specific clinical and technical situations. In addition, the importance of offering practical sessions to improve maintenance and troubleshooting skills is highlighted.
Manuals and Training Resources:
The provision of detailed manuals and reference documents is key for staff, complemented by the use of online platforms that facilitate the distribution of training resources, instructional videos, and educational materials.
Knowledge Management:
Knowledge management involves maintaining an up-to-date knowledge base with relevant technical information. In addition, the importance of facilitating collaboration between staff to share experiences and technical knowledge is highlighted.
Security and Compliance Training:
Security and compliance training involves providing training on security and privacy measures related to the handling of medical equipment. The importance of ensuring that staff are aware of the relevant rules and regulations in the healthcare sector is also highlighted.
The effective combination of technical support and training ensures that Clinical Engineering staff have the skills and support necessary to efficiently and safely maintain and manage medical equipment in healthcare settings.
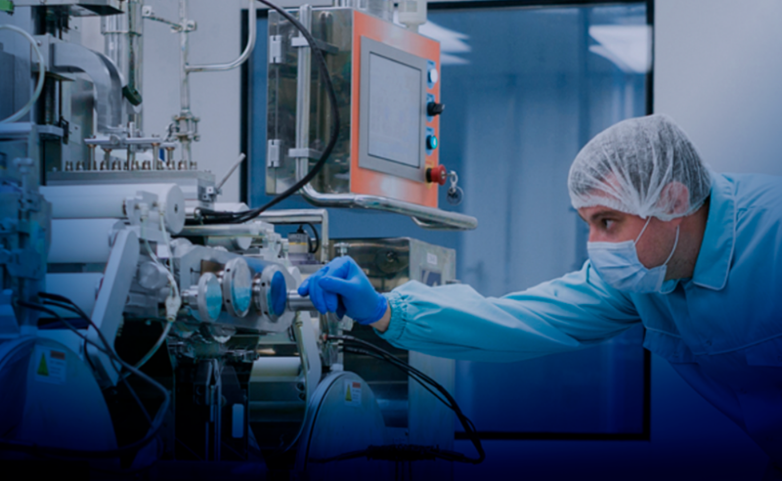

Risk management in Clinical Engineering:
Risk management in Clinical Engineering is a fundamental component to ensure the safety of patients, medical staff and the efficient operation of medical equipment in healthcare settings. Key aspects related to risk management in this context are described here:
Medical Equipment Assessment:
Medical equipment assessment involves performing detailed risk assessments for each piece of equipment, with the goal of identifying potential failures, malfunctions, or risks associated with the use of the devices.
Previous Event Review:
The review of previous events consists of analyzing previous adverse events or incidents with the purpose of learning from past experiences. It seeks to identify patterns and areas for improvement based on previous events to strengthen management and prevention of similar problems in the future.
New Technology Assessment:
The assessment of new medical technologies involves analyzing the risks associated with their implementation. Aspects such as interoperability, cybersecurity, and staff training must be considered to ensure successful and safe adoption of new technologies.
Technical Risk Analysis:
Technical risk analysis involves evaluating potential equipment failures or malfunctions through a risk analysis. Factors such as obsolescence, reliability, and availability are considered in this process to anticipate and manage technical risks associated with the equipment.
Controlled Change Management:
Controlled change management involves establishing controlled processes for the implementation of changes to medical equipment. It is crucial to assess and mitigate risks prior to the introduction of modifications, ensuring a structured and cautious approach to change management to ensure the safety and effectiveness of equipment.
Adherence to Regulations:
Adherence to regulations in Clinical Engineering involves ensuring that all practices comply with relevant regulations and standards. It is essential to maintain detailed records as evidence to demonstrate compliance with established standards.
Threat Protection:
Threat protection in Clinical Engineering involves the implementation of cybersecurity measures to protect medical equipment from potential threats. In addition, the importance of performing regular updates to systems to address and mitigate potential vulnerabilities is highlighted.
Risk management in Clinical Engineering is an ongoing process that requires collaboration between healthcare professionals, biomedical engineers, and risk management personnel. Early identification, accurate assessment, and effective mitigation of risks are essential to maintaining a safe and efficient healthcare environment.

Frequently asked questions about the Clinical Engineering department:
What functions does the Department of Clinical Engineering perform?
The Clinical Engineering Department is responsible for the management, maintenance and assurance of medical technology, guaranteeing its safe and efficient operation in clinical environments.
What is the role of clinical engineers in a hospital?
Clinical engineers monitor, maintain, and manage medical equipment, perform safety inspections, and collaborate with medical staff to optimize the use of technology in patient care.
How does the Clinical Engineering Department ensure the safety of medical equipment?
We perform regular inspections, safety testing and preventative maintenance. We also work closely with manufacturers to follow best practices and regulations.
What training is required to become a clinical engineer?
A bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering or a related discipline is generally required. Many clinical engineers also earn specific certifications in medical technology management.
How are upgrades and new acquisitions of medical equipment managed?
We constantly assess needs, conduct cost-benefit analyses, participate in acquisition planning, and collaborate with other departments to ensure efficient implementation.
What measures does the Clinical Engineering Department take to ensure regulatory compliance?
We conduct internal audits, follow industry standards and stay up to date on local and international regulations related to medical technology.
How are emergencies involving medical equipment handled?
We have emergency response procedures, rapid response teams and collaborate with other departments to ensure an effective response in critical situations.
What is the role of information technology in Clinical Engineering?
Information technology is crucial for managing medical equipment databases, maintenance information systems, and integrating network technologies.
How is the performance and efficiency of medical equipment measured?
We conduct performance evaluations, key indicator monitoring and data collection to assess the efficiency and profitability of medical equipment.
What advice would you give for the efficient management of medical technology in a clinical environment?
Maintain a preventative maintenance program, encourage ongoing staff training, establish safety protocols, and work closely with manufacturers and other hospital departments.
Conclusion on the Clinical Engineering department:
The Clinical Engineering Department plays a key role in technological management and support in the hospital environment. From the acquisition and maintenance of medical equipment to technical support and risk management, this department contributes to ensuring the quality of medical care and patient safety. Effective collaboration with other departments and monitoring the latest technological trends are key to success and efficiency in the delivery of healthcare services.
Recommendation:
To deepen your knowledge of clinical engineering, I suggest you continue reading the next article that addresses: What are bioelectrodes in Clinical Engineering?





0 Comments